UPSC Essentials | Mains answer practice — GS 1 : Questions on land subsidence and historical significance of the Tea Horse Road (Week 92)
Are you preparing for CSE 2025? Here are questions from GS paper 1 for this week with essential points as the fodder for your answers. Do not miss points to ponder and answer in the comment box below.
 Attempt a question on the land subsidence and the causes of land subsidence in today's answer writing practice. (PTI)
Attempt a question on the land subsidence and the causes of land subsidence in today's answer writing practice. (PTI)UPSC Essentials brings to you its initiative for the practice of Mains answer writing. It covers essential topics of static and dynamic parts of the UPSC Civil Services syllabus covered under various GS papers. This answer-writing practice is designed to help you as a value addition to your UPSC CSE Mains. Attempt today’s answer writing on questions related to topics of GS-1 to check your progress.
🚨 Click Here to read the Union Budget Special issue of the UPSC Essentials magazine for February 2025. Share your views and suggestions in the comment box or at manas.srivastava@indianexpress.com🚨
QUESTION 1
Discuss the historical significance of the Tea Horse Road in facilitating trade and cultural exchanges between China, Tibet, and India.
QUESTION 2
What is land subsidence? What are the causes of land subsidence? Give examples.
General points on the structure of the answers
Introduction
— The introduction of the answer is essential and should be restricted to 3-5 lines. Remember, a one-liner is not a standard introduction.
— It may consist of basic information by giving some definitions from the trusted source and authentic facts.
Body
— It is the central part of the answer and one should understand the demand of the question to provide rich content.
— The answer must be preferably written as a mix of points and short paragraphs rather than using long paragraphs or just points.
— Using facts from authentic government sources makes your answer more comprehensive. Analysis is important based on the demand of the question, but do not over analyse.
— Underlining keywords gives you an edge over other candidates and enhances presentation of the answer.
— Using flowcharts/tree-diagram in the answers saves much time and boosts your score. However, it should be used logically and only where it is required.
Way forward/ conclusion
— The ending of the answer should be on a positive note and it should have a forward-looking approach. However, if you feel that an important problem must be highlighted, you may add it in your conclusion. Try not to repeat any point from body or introduction.
— You may use the findings of reports or surveys conducted at national and international levels, quotes etc. in your answers.
Self Evaluation
— It is the most important part of our Mains answer writing practice. UPSC Essentials will provide some guiding points or ideas as a thought process that will help you to evaluate your answers.
THOUGHT PROCESS
You may enrich your answers by some of the following points
QUESTION 1: Discuss the historical significance of the Tea Horse Road in facilitating trade and cultural exchanges between China, Tibet, and India.
Note: This is not a model answer. It only provides you with thought process which you may incorporate into the answers.
Introduction:
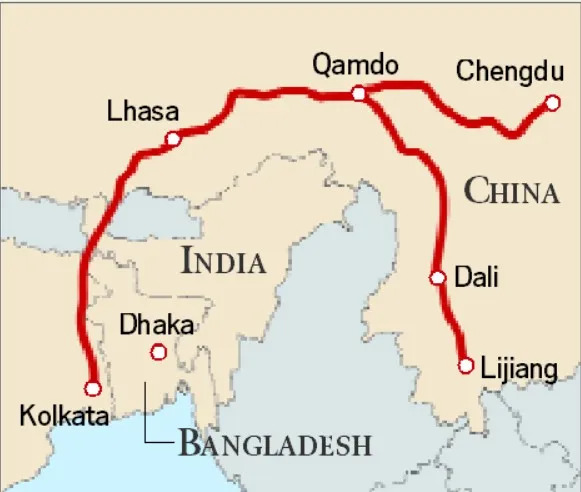
— The term “Tea Horse Road” refers to a network of branching paths that began in southwest China and finished in the Indian subcontinent.
— The two main routes crossed via cities such as Dali and Lijiang in Yunnan province, as well as Lhasa in Tibet, before crossing the Indian subcontinent and branching out into modern-day India, Nepal, and Bangladesh. These roads were dangerous to travel on, passing through harsh terrain and reaching elevations of up to 10,000 feet.
Body:
You may incorporate some of the following points in your answer:
— The Tea Horse Road originated during the Tang dynasty’s administration in China (618-907 CE). The writings of Buddhist monk Yijing (635-713 CE), who provided some of the most detailed descriptions of Nalanda university available today, mention the transportation of sugar, textiles, and rice noodles from southwestern China to Tibet and India, as well as horses, leather, Tibetan gold, saffron, and other medicinal herbs to China.
— According to official archives from the Song dynasty (960-1279 CE), the commerce gradually shifted towards teas and horses. However, traders would use the route to trade other items as well, not always covering the complete path to South Asia.
 Tea Horse Road, 1908 map (Wikimedia Commons)
Tea Horse Road, 1908 map (Wikimedia Commons)
Importance of Tea Horse Road
— The primary motivation of the road is thought to be the desire for tea among Tibetan nomads.
— Tibetan princes and nomads alike embraced tea for excellent reasons. It was a hot beverage in a frigid area when the only alternatives were snowmelt, yak or goat milk, barley milk, or chang. A cup of yak butter tea, with its peculiar salty, somewhat oily, sharp flavour, served as a mini-meal for herders huddled around yak dung fires in a windy wilderness.
— Horses were an important military resource and mode of transportation. However, horses were not produced in China’s central plains, so they had to be imported from adjacent Tibet and Yunnan provinces.
— The geographical characteristics of the commercial items tea and horse, in this situation, encouraged complementary trade activities, resulting in the formation of the tea and horse exchange market.
Conclusion:
— In 1912, as the reign of the Qing dynasty drew to an end, the Horse Tea Road would continue to stay significant. Domestic “turmoil and foreign aggressions” presented a “unique opportunity for the trading systems in southwest China”.
— Later, during World War II, the route was critical in bringing supplies to the frontline conflict in China, where Japan controlled nearly all of the Chinese shoreline and airspace.
— With the formation of the People’s Republic in 1949, the Tea Horse Road gradually declined. Roads were paved and contemporary construction was undertaken, and just a few trails remain today.
(Source: How the historic Tea Horse Road connected India to China, through Tibet by Rishika Singh)
Points to Ponder
Read more about Tea Horse Road
Read about Silk Road
Related Previous Year Question
Why was indentured labour taken by the British from India to other colonies? Have they been able to preserve their cultural identity over there? (2018)
QUESTION 2: What is land subsidence? What are the causes of land subsidence? Give examples.
Note: This is not a model answer. It only provides you with thought process which you may incorporate into the answers.
Introduction:
— Land subsidence is the slow or sudden sinking of the earth’s surface.
— Subsidence, or ground sinking due to underground material movement, is most commonly induced by the extraction of water, oil, natural gas, or mineral resources from the earth by pumping, fracking, or mining activities.
— Subsidence is an unavoidable result of ground movement produced by a variety of artificial and natural forces. Economic prosperity from the exploitation of the earth’s buried resources is invariably accompanied with the negative consequences of subsidence.
Body:
You may incorporate some of the following points in your answer:
Causes of land subsidence
— Natural events might also cause subsidence such as:
earthquakes;
soil compaction;
the glacial isostatic adjustment;
erosion;
sinkhole Formation, and
adding water to fine soils deposited by the wind.
— Subsidence can occur in very vast areas, such as entire states or provinces, or in very small areas, such as a section of your backyard.
— It can be induced by a combination of sediment loading (when rivers deposit silt in an area, which then sinks due to the added weight) and sediment compaction following groundwater removal.
Examples
— Joshimath land subsidence: Some experts suggest that the incident might have occurred because of unplanned construction, over-population, obstruction of the natural flow of water and hydel power activities.
— Bageshwar (vulnerable to land subsidence): Due to unregulated soapstone mining.
— Iraqi region sinking: The region surrounding the Zagros Mountains in the country’s north is sinking. A growing tear is forming in a region along the Arabian and Eurasian continental plates known as the Neotethys oceanic slab.
(Source: Why Iraq is (slowly) sinking into Earth, Joshimath crisis: What is land subsidence and why does it happen?, How soapstone mining is leading to land-subsidence in Uttarakhand’s Bageshwar, oceanservice.noaa.gov)
Points to Ponder
How can the problem of land subsidence be controlled?
Read more examples about land subsidence around the world
Related Previous Year Questions
Differentiate the causes of landslides in the Himalayan region and Western Ghats. (2021)
“The Himalayas are highly prone to landslides.” Discuss the causes and suggest suitable measures of mitigation. (2016)
Previous Mains Answer Practice
UPSC Essentials: Mains answer practice — GS 3 (Week 92)
UPSC Essentials: Mains answer practice — GS 3 (Week 91)
UPSC Essentials: Mains answer practice — GS 2 (Week 92)
UPSC Essentials: Mains answer practice — GS 2 (Week 91)
UPSC Essentials: Mains answer practice — GS 1 (Week 91)
UPSC Essentials: Mains answer practice — GS 1 (Week 89 and 90)
Subscribe to our UPSC newsletter and stay updated with the news cues from the past week.
Stay updated with the latest UPSC articles by joining our Telegram channel – IndianExpress UPSC Hub, and follow us on Instagram and X.
Must Read


Buzzing Now
Mar 14: Latest News
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
































